Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maruyama, Shuhei; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1372 - 1385, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kubo, Kotaro; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.359 - 373, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:78.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is an essential approach to improving the safety of nuclear power plants. However, this method includes certain difficulties, such as modeling of combinations of multiple hazards. Seismic-induced flooding scenario includes several core damage sequences, i.e., core damage caused by earthquake, flooding, and combination of earthquake and flooding. The flooding fragility is time-dependent as the flooding water propagates from the water source such as a tank to compartments. Therefore, dynamic PRA should be used to perform a realistic risk analysis and quantification. This study analyzed the risk of seismic-induced flooding events by coupling seismic, flooding, and thermal-hydraulics simulations, considering the dependency between multiple hazards explicitly. For requirements of safety improvement, especially in light of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, sensitivity analysis was performed on the seismic capacity of systems, and the effectiveness of alternative steam generator injection by a portable pump was estimated. We demonstrate the use of this simulation-based dynamic PRA methodology to evaluate the risk induced by a combination of hazards.
Kubo, Kotaro; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.357 - 367, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:65.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA), which handles epistemic and aleatory uncertainties by coupling the thermal-hydraulics simulation and probabilistic sampling, enables a more realistic and detailed analysis than conventional PRA. However, enormous calculation costs are incurred by these improvements. One solution is to select an appropriate sampling method. In this paper, we applied the Monte Carlo, Latin hypercube, grid-point, and quasi-Monte Carlo sampling methods to the dynamic PRA of a station blackout sequence in a boiling water reactor and compared each method. The result indicated that quasi-Monte Carlo sampling method handles the uncertainties most effectively in the assumed scenario.
Ikenoue, Tsubasa; Shimadera, Hikari*; Kondo, Akira*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 225, p.106452_1 - 106452_12, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.71(Environmental Sciences)This study focused on the uncertainty of the factors of the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) and evaluated its impacts on the environmental fate of  Cs simulated by a radiocesium transport model in the Abukuma River basin. The USLE has five physically meaningful factors: the rainfall and runoff factor (R), soil erodibility factor (K), topographic factor (LS), cover and management factor (C), and support practice factor (P). The simulation results showed total suspended sediment and
Cs simulated by a radiocesium transport model in the Abukuma River basin. The USLE has five physically meaningful factors: the rainfall and runoff factor (R), soil erodibility factor (K), topographic factor (LS), cover and management factor (C), and support practice factor (P). The simulation results showed total suspended sediment and  Cs outflows were the most sensitive to C and P among the all factors. Therefore, land cover and soil erosion prevention act have the great impact on outflow of suspended sediment and
Cs outflows were the most sensitive to C and P among the all factors. Therefore, land cover and soil erosion prevention act have the great impact on outflow of suspended sediment and  Cs. Focusing on land use, the outflow rates of
Cs. Focusing on land use, the outflow rates of  Cs from the forest areas, croplands, and undisturbed paddy fields were large. This study indicates that land use, especially forest areas, croplands, and undisturbed paddy fields, has a significant impact on the environmental fate of
Cs from the forest areas, croplands, and undisturbed paddy fields were large. This study indicates that land use, especially forest areas, croplands, and undisturbed paddy fields, has a significant impact on the environmental fate of  Cs.
Cs.
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Muramatsu, Ken*; Takada, Tsuyoshi*
Nihon Jishin Kogakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 20(2), p.2_1 - 2_16, 2020/02
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(4), p.345 - 354, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Particle transport simulations based on the Monte Carlo method have been applied to shielding calculations. Estimation of not only statistical uncertainty related to the number of trials but also systematic one induced by unclear physical quantities is required to confirm the reliability of calculated results. In this study, we applied a method based on analysis of variance to shielding calculations. We proposed random- and three-condition methods. The first one determines randomly the value of the unclear quantity, while the second one uses only three values: the default value, upper and lower limits. The systematic uncertainty can be estimated adequately by the random-condition method, though it needs the large computational cost. The three-condition method can provide almost the same estimate as the random-condition method when the effect of the variation is monotonic. We found criterion to confirm convergence of the systematic uncertainty as the number of trials increases.
Uchida, Shunsuke; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Naito, Masanori*; Kojima, Masayoshi*; Kikura, Hiroshige*; Lister, D. H.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 341, p.112 - 123, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Improvement of plant reliability based on reliability-centered-maintenance (RCM) is going to be undertaken in NPPs. RCM is supported by risk-based maintenance (RBM). The combination of prediction and inspection is one of the key issues to promote RBM. Early prediction of IGSCC occurrence and its propagation should be confirmed throughout the entire plant systems which should be accomplished by inspections at the target locations followed by timely application of suitable countermeasures. From the inspections, accumulated data will be applied to confirm the accuracy of the code, to tune some uncertainties of the key data for prediction, and then, to increase their accuracy. The synergetic effects of prediction and inspection on application of effective and suitable countermeasures are expected. In the paper, the procedures for the combination of prediction and inspection are introduced.
 for MYRRHA using a Monte Carlo technique
for MYRRHA using a Monte Carlo techniqueIwamoto, Hiroki; Stankovskiy, A.*; Fiorito, L.*; Van den Eynde, G.*
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 4, p.42_1 - 42_7, 2018/11
This paper presents a nuclear data sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of the effective delayed neutron fraction  for critical and subcritical cores of the MYRRHA reactor using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo transport code MCNP. The
for critical and subcritical cores of the MYRRHA reactor using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo transport code MCNP. The  sensitivities are calculated by the modified
sensitivities are calculated by the modified  -ratio method proposed by Chiba. Comparing the
-ratio method proposed by Chiba. Comparing the  sensitivities obtained with different scaling factors
sensitivities obtained with different scaling factors  introduced by Chiba shows that a value of
introduced by Chiba shows that a value of 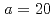 is the most suitable for the uncertainty quantification of
is the most suitable for the uncertainty quantification of  . Using the calculated
. Using the calculated  sensitivities and the JENDL-4.0u covariance data, the
sensitivities and the JENDL-4.0u covariance data, the  uncertainties for the critical and subcritical cores are determined to be 2.2
uncertainties for the critical and subcritical cores are determined to be 2.2  0.2% and 2.0
0.2% and 2.0  0.2%, respectively, which are dominated by delayed neutron yield of
0.2%, respectively, which are dominated by delayed neutron yield of  Pu and
Pu and  U.
U.
Honda, Yuki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 4(3), p.031013_1 - 031013_11, 2018/07
There is growing interest in uncertainty analysis for probabilistic risk assessment (PRA). The focus of this research is to propose and trial investigate the new approach which identify influencing factors for uncertainty in a systematic manner for High Temperature Gas -cooled Reactor (HTGR). As a trial investigation, this approach is tested to evaluation of maximum fuel temperature in a depressurized loss-of-forced circulation (DLOFC) accident and failure of mitigation systems such as control rod systems from the view point of reactor dynamics and thermal hydraulic characteristics. As a result, 16 influencing factors are successfully selected in accordance with the suggested procedure. In the future, the selected influencing factors will be used as input parameter for uncertainty propagation analysis.
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Li, Y.; Muramatsu, Ken*; Takada, Tsuyoshi*
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
After the 2011 Fukushima accident, nuclear power plants are required to take countermeasures against accidents beyond design basis conditions. In seismic probabilistic risk assessment (SPRA), uncertainty can be classified as either aleatory uncertainty, which cannot be reduced, or epistemic uncertainty, which can be reduced with additional knowledge and/or information. To improve the reliability of SPRA, efforts should be made to identify and reduce the epistemic uncertainty caused by the lack of knowledge. In this study, we focused on the difference in seismic response by modeling methods, which is related epistemic uncertainty. We conducted a seismic response analysis with two kinds of modeling methods; a three-dimensional finite-element model and a conventional sway-rocking stick model, by using simulated various input ground motions, which is related to aleatory uncertainty. And then we quantified the seismic floor response results of the various input ground motions of each modeling methods. For the uncertainty quantification related to different modeling methods, we further perform a statistical analysis of the floor response results of the nuclear reactor building. Finally, we discussed how to utilize the results from these calculations for the quantification of uncertainty in fragility analysis for SPRA.
Zheng, X.; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2017/11
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Muramatsu, Ken*; Takada, Tsuyoshi*
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Structural Safety & Reliability (ICOSSAR 2017) (USB Flash Drive), p.2206 - 2213, 2017/08
In order to clarify the influence of the difference of modeling method on the variation of the result of seismic response analysis of nuclear facility, seismic response analysis using various simulated input ground motions was carried out and the sensitivity analyses of the variations in seismic response was conducted. In particular, we focused on the maximum acceleration response of reactor building shear walls, the effect of modeling method on response result and the factors of response variation were described and discussed.
Honda, Yuki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/07
There is growing interest in uncertainty analysis for probabilistic risk assessment (PRA). Our target is the uncertainty analysis method development for depressurized loss-of-forced circulation (DLOFC) accident with failure of control rod systems (CRS). As one of key elements, this paper focuses on the quantification of uncertainty for the fuel temperature which is dominant for a source term analysis. As an initial step, this paper aims to suggest a procedure to identify influencing factors which is input parameter for uncertainty analysis, and shows the results of derivation of variable parameters by expansion of dynamic equation and extraction of uncertainties in variable factors.
Nakajima, Norihiro; Nishida, Akemi; Miyamura, Hiroko; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Kashika Joho Gakkai-Shi (USB Flash Drive), 36(Suppl.2), 4 Pages, 2016/10
Since nuclear power plants have dimensions approximately 100m and their structures are an assembly made up of over 10 million components, it is not convenient to experimentally analyze its behavior under strong loads of earthquakes, due to the complexity and hugeness of plants. The proposed system performs numerical simulations to evaluate the behaviors of an assembly like a nuclear facility. The paper discusses how to carry out visual analysis for assembly such as nuclear power plants. In a result discussion, a numerical experiment was carried out with a numerical model of High Temperature engineering Test Reactor of Japan Atomic Energy Agency and its result was compared with observed data. A good corresponding among them was obtained as a structural analysis of an assembly by using visualization. As a conclusion, a visual analytics methodology for assembly is discussed.
and their structures are an assembly made up of over 10 million components, it is not convenient to experimentally analyze its behavior under strong loads of earthquakes, due to the complexity and hugeness of plants. The proposed system performs numerical simulations to evaluate the behaviors of an assembly like a nuclear facility. The paper discusses how to carry out visual analysis for assembly such as nuclear power plants. In a result discussion, a numerical experiment was carried out with a numerical model of High Temperature engineering Test Reactor of Japan Atomic Energy Agency and its result was compared with observed data. A good corresponding among them was obtained as a structural analysis of an assembly by using visualization. As a conclusion, a visual analytics methodology for assembly is discussed.
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Itoi, Tatsuya*; Takada, Tsuyoshi*; Furuya, Osamu*; Muta, Hitoshi*; Muramatsu, Ken
Proceedings of 13th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (PSAM-13) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2016/10
In this study, we address epistemic uncertainty in structure fragility estimation of nuclear power plants (NPPs). In order to identify and quantify dominant factors in fragility assessment, sensitivity analyses of seismic analysis results are conducted for a target NPP building using a three-dimensional finite element model and a conventional lumped mass model (embedded sway rocking model), and the uncertainty caused by the major factors is then evaluated. The results are used to classify epistemic uncertainty levels in a fragility estimation workflow for NPPs in several stages, and a graded knowledge tree technique, which can be used for future fragility estimations, is proposed.
Zheng, X.; Ito, Hiroto; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Maruyama, Yu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(3), p.333 - 344, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:68.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)Mascari, F.*; Nakamura, Hideo; Umminger, K.*; De Rosa, F.*; D'Auria, F.*
Proceedings of 16th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-16) (USB Flash Drive), p.4921 - 4934, 2015/08
Zheng, X.; Ito, Hiroto; Kawaguchi, Kenji; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Maruyama, Yu
Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 138, p.253 - 262, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:39.94(Engineering, Industrial)Nakajima, Norihiro; Nishida, Akemi; Kawakami, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Yoshio; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Iigaki, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
A numerical analysis controlling and managing system is implemented on K, which controls the modelling process and data treating, although the manager only controls a structural analysis by finite element method. The modeling process is described by the list of function ID and its procedures in a data base. The manager executes the process by order in the list for simulation procedures. The manager controls the intention of an analysis by changing the analytical process one to another. Experiments were carried out with static and dynamic analyses.
Homma, Toshimitsu; Liu, X.; Tomita, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM-5), p.2753 - 2758, 2000/00
no abstracts in English